Introduction
Node-RED is a programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs and online services in new and interesting ways.

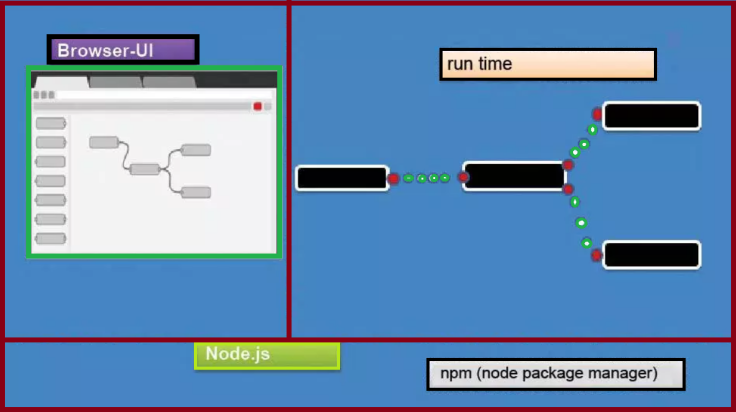
It provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its runtime in a single-click.
Since early 2014, the mobile has overtaken the personal computer (desktop/laptop) as the leading device used to navigate the Internet. Along with the mobile, a number of other portable devices that connect to the Internet have also started proliferating at a very quick rate. Nowadays, most of us carry or possess at least one Internet based device and a mobile. So, the Internet of Things (IoT) now doesn’t only mean different ‘things’, but has evolved into ‘intelligent things’ which have on-board computation and network connections. Most importantly, they have the capability to sense the environment around us and, accordingly, act intelligently. These devices are now referred to as connected devices, smart objects or the Web of Things.
This adaptation of technology has led to many developments in the visual programming and visual coding arenas. As a result, Node-RED has evolved into a visual programming/coding tool based on the already popular Node.js (a server side Java Scripting platform), mainly targeting the Internet of Things space
Features of Node-RED
The major features of Node-RED are listed below.
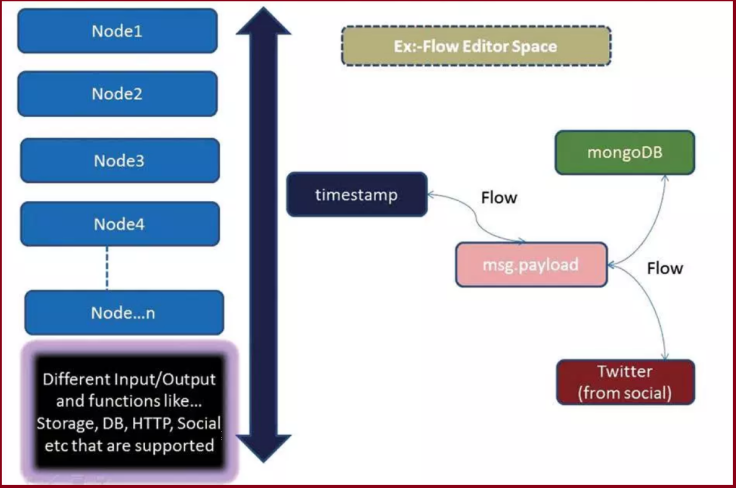
- It supports browser-based flow editing.
- As it is built on Node.js, it supports a lightweight runtime environment along with the event driven and non-blocking model.
- The various flows created in Node-RED are stored using JSON, which can be easily imported and exported for sharing with others.
- You can run it locally (Docker support, etc).
- It can easily fit on most widely used devices like Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone Black, Arduino, Android based devices, etc.
- It can run in the cloud environment like Bluemix, AWS, MS-Azure, etc.
Node-RED architecture
Some of the key aspects of Node-RED architecture are listed below:
- Node-RED is fast because it is driven by the latest supported version of Node.js
- Asynchronous io and event-driven architecture.
- Single-threaded event queue, which supports simplicity.
- Single language support for JavaScript (both from front-end and back-end).
- Complete architecture has been built using express, d3, jquery and ws.
Different types of nodes
Inject node
- This node allows manual triggering of flows.
- It helps us to inject events at scheduled intervals.
Debug node
- The debug node helps in displaying the contents of a message—either the payload or the entire object.
Template node
- Modifies the output based on a Mustache (logic-less) template.
Other than the above, there are various input, output and function nodes, like:
a. Input nodes:
- HTTP
- IBM IoT
b. Output nodes:
- HTTP response
- IBM IoT
- Twilio (send SMSs using the Twilio service)
c. Function nodes:
- Function
- Switch
Running Node-RED
Once the Node-RED installation and initial configuration is done, it is ready to be deployed or used. There are three ways in which Node-RED can be run:
- Locally (Docker-container)
- On a device (Raspberry-Pi, Arduino, Android based devices, etc)
- In the identified cloud environment
Where can Node-RED be used?
Node-RED can be used in a range of applications. The major ones are listed below.
- In Bluemix, for connecting to IoT (with ReST and MQTT).
- For binding and connecting to databases (MongoDB).
- For storing IoT data for present and future computation.
- For social media, when taking action and when event driven applications are needed (like Twitter).
Node-RED has over 225,000 package repos, to which it is easy to extend and add new packages. It also has a dedicated community, and is built with robust architecture using Node.js (which is very popular these days).
Node-RED can be used in event driven and fast-to-market applications and services, with easily implementable steps.
Leave a comment